Animal Production, The continuous growth and transformation of the livestock sector offer substantial opportunities for agricultural development, poverty reduction, food security gains and improved human nutrition.
Animal Production – Agricultural Sciences Grade 12 Questions and Answers
QUESTIONS
- Answer the questions below. Check your answers afterwards and do corrections.
- Give yourself one hour.
- Marks: 100
- List the FOUR main factors that can be addressed to increase the production of any farming system. (4)
- Explain why free range pig and poultry systems are considered to be more humane than intensive farming systems. (4)
- State FOUR environmental problems that can occur in closed houses. (4)
- Mention THREE practical methods that can be used to provide shade for farm animals. (3)
- Identify TWO harmful effects of the cold on farm animals. (4)
- Which farm animals are most susceptible to the cold? (2)
- Describe methods could you use to prevent pigs from overheating and getting sunburned in free range systems. (3)
- Name THREE energy efficient ways to control the temperature in closed animal houses. (3)
- Discuss the importance of well-designed feeders in closed animal houses. (4)
- Identify the production system in the diagram and explain how it functions. (8)
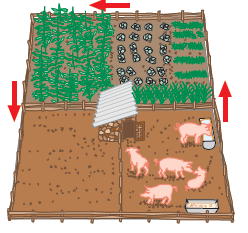
- Discuss why artificial lighting is used in commercial layer houses. (5)
- Identify the basic requirements of a free range dairy. (10)
- Explain the significance of following types of animal behaviour:
13.1 dominance/submission
13.2 courtship
13.3 pecking order
13.4 grooming. (8) - Which ONE of the following is INCORRECT with respect to the precautions that need to be considered when livestock is transported to an abattoir?
14.1 Different types of animals should NOT be transported together.
14.2 Pregnant and injured animals should NOT be transported.
14.3 Animals of different ages and sexes should NOT be transported together.
14.4 Air and light should NOT be allowed to enter the part of the truck where animals are kept. (2) - Name four signs of aggression in bulls and cows with calves. (4)
- Name three golden rules which sum up how we should work with farm animals. (3)
- List FOUR uses of rope in farm animal handling. (8)
- You need to examine the tongues of cattle for a foot and mouth inspection campaign. Name the tools/aids that you could use to immobilise their heads. (6)
- Give ONE word/term/phrase for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term/phrase next to the question number.
19.1 A place in the handling facility where cattle are kept during the handling process to avoid injuries. (2)
19.2 A relatively small area where a large number of animals are kept and fed for optimal production purposes. (2) - List five basic requirements of a vehicle used to transport farm animals. (5)
- Chicks in intensive broiler houses often die purely from management problems. List at least six causes of chick deaths which can be caused by management factors. (6)
ANSWERS
- Nutrition, breeding, environment, general management. (4)
- More natural – space, sunlight, prevent boredom, exercise. (4)
- Poor ventilation, wet bedding, crowding, build-up of micro-organisms. (4)
- Trees, shade cloth, open housing (any other suitable point). (3)
- Fatal hypothermia, energy use, disease (any two). (4)
- Pigs and chickens (2)
- Open house to provide shade, mud wallow or hosepipe/ sprinkler systems. (3)
- Insulation, N/S orientation of long side, good air flow design. (3)
- Feed is biggest expense of all input costs therefore one must prevent waste and fouling. (4)
- Free range pig production systems provide a shelter and open pens. Sometimes they also provide pigs with a mud wallow or a sprinkler system to keep them cool. The shelter is in the form of permanent open-sided houses or mobile houses like corrugated barrels. The pigs use the pens to move around in, rootle in soil and to defecate. The pens can be rotated around the house or the house can be moved to keep the pen area hygienic. Crops can be planted where the pigs have fertilised the soil. Pigs can forage for some of their food but they can also be provided with feed.
The amount of feed given will depend on the level of production. (8) - Egg production drops in response to the decreased daylight hours in autumn/winter so providing extra light hours during this season keeps constant production. (5)
- Camps, holding pens, crush, foot bath, parlour with roof, washable sloping non-slip floors, milk stalls, milk room, calf houses. (10)
- Briefly explain the following types of animal behaviour:
13.1 Dominance is when a particular animal heads the hierarchy in the group; submissive behaviour: individual animal tried to appease an dominant one through behaviour such as infantile behaviour or exposing its most vulnerable spot, such as the throat, to the dominant animal
13.2 Carried out to attract a partner/indicates being on heat
13.3 Most directly related to social organisation of chickens, but is also applied to social organisation among other groups as well; dominant animals ‘peck’ those that are less dominant, all the way from the most to the least dominant
13.4 Refers to animals cleaning/looking after themselves or one another. (8) - Air and light should NOT be allowed to enter the part of the truck where animals are kept. (2)
- Pawing ground, snorting, bellowing, charging. (4)
- Stay calm, quiet, and slow. (3)
- Cattle-leading; restraining; hobbling at milking; lifting hooves; pigs-snout snare (any four) (8)
- Halters, nose tongs, head clamps. (6)
- ONE word/term/phrase for each of the following descriptions.
19.1 Holding pen/crush. (2)
19.2 Feedlot. (2) - Clean, non-slip surface, separate crates for different ages, good ventilation and light. (5)
- Overcrowding, causing hygiene problems such as a build-up of ammonia from the faeces of large numbers of birds; poorly ventilated, causing respiratory problems; insufficient feeders and watering points for the number of birds in the house; high concentration of birds; failure to develop and implement an intensive vaccination and medication programme.


