The organelle through which water and carbon dioxide enter the leaf of a plant. Leaves also have specialized openings called stomata. These are small adjustable pores that can open and close to allow gas to enter and exit the plant. For photosynthesis to occur, the stomata open and allow carbon dioxide to enter the plant.
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. It is a passive process that requires no energy expense by the plant. Transpiration also cools plants, changes osmotic pressure of cells, and enables mass flow of mineral nutrients

The organelle through which water and carbon dioxide enter the leaf of a plant is called the stomata.
What Stomata is
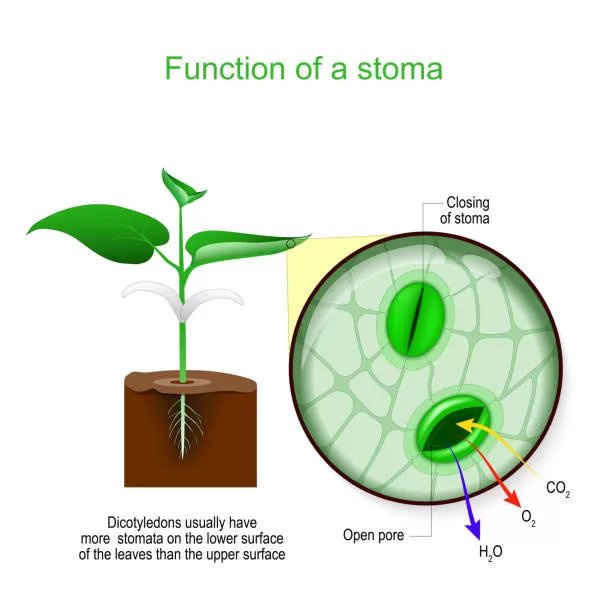
A stomata is a small opening found on the surface of leaves, stems, and other plant organs that is used for gas exchange. It is composed of two guard cells, which are specialized cells that control the opening and closing of the stomatal pore. When the guard cells absorb water, they swell and cause the stomatal opening to widen, allowing for the exchange of gases such as carbon dioxide and oxygen. The stomata also play a role in regulating the plant’s water balance by controlling the amount of water lost through transpiration. They are essential for the process of photosynthesis, as they allow the plant to take in carbon dioxide from the air to be used in the production of energy.
Examples of plants that have stomata
- Oaktree
- Maple tree
- Tomato plant
- Sunflower
- Cactus
- Pine tree
Video: Stomata | Opening and Closing of Stomata
Common questions and answers about Stomata
Q: What is the function of stomata in plants? A: The main function of stomata is to allow plants to take in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis and to release oxygen and water vapor.
Q: How do stomata open and close? A: Stomata open and close through the movement of guard cells, which are specialized cells found near the stomatal opening. When the guard cells absorb water, they swell and cause the stomatal opening to widen, allowing for gas exchange. When the guard cells lose water, they shrink and the stomatal opening closes.
Q: Why are stomata found primarily on the lower surface of leaves? A: Stomata are typically found on the lower surface of leaves to reduce water loss through transpiration. The upper surface of leaves is exposed to more sunlight and heat, which can cause increased water loss through evaporation.
Q: Can stomata be found on other plant organs besides leaves? A: Yes, stomata can also be found on the stems, flowers, and fruits of some plants.
Q: What happens when stomata are closed? A: When stomata are closed, the plant is not able to take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and release oxygen. This can limit the plant’s growth and survival in low light or dry conditions.
