Menstrual cycle Grade 12 Life Sciences Notes with Activities Questions and Answers. In a life cycle, a woman’s body is vulnerable to a variety of changes. The cycle of these changes occur in women every month, positively for pregnancy is called the menstrual cycle. When an ovum is unfertilized, the uterus lining sheds and leads to a haemorrhage, called menstruation.
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
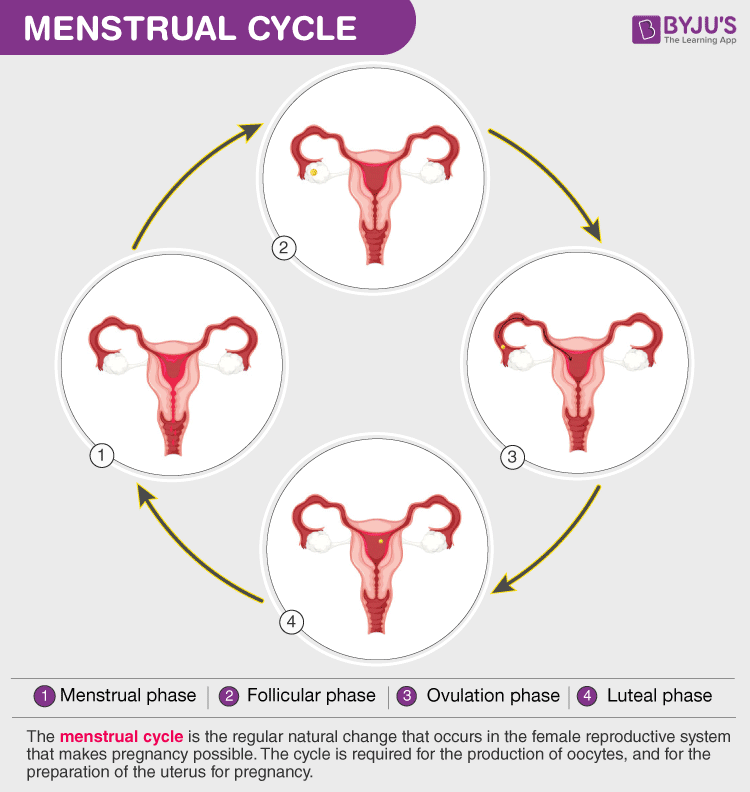
The menstrual cycle is divided into four phases, namely:
- Menstrual phase: Day 1, uterus lining which is prepared for implantation starts to shed which lasts 3 to 5 days.
- Follicular phase: In this phase, the primary follicle starts developing into a mature Graffian follicle. The endometrium also starts proliferating. The uterus starts preparation for another pregnancy.
- Ovulatory phase: Mid-cycle phase, this is the phase in which ovulation takes place i.e., day 13-17. The end of the follicular phase along with the ovulation period defines the fertilisation period.
- Luteal phase: It is the post-ovulation phase, where the fate of the corpus luteum is decided. If fertilisation occurs, pregnancy starts. If fertilisation doesn’t occur, it marks the onset of another cycle.
Menstrual Cycle Diagram
Menstrual cycle Grade 12 Life Sciences Notes
Day 1–7
- Ovaries: New follicles develop and secrete oestrogen
- Uterus: Lining breaks down and is released (menstruation)
Day 8–13
Ovaries: Mature Graafian follicle develops:
- The Graafian follicle moves to edge of the ovary
- It secretes oestrogen
Uterus: Oestrogen stimulates the endometrium to become thicker and develop more blood vessels and glands
Day 14
Ovaries: Graafian follicle bursts to release an egg cell. The process is called ovulation
Day 15–22
- Ovaries: The Graafian follicle becomes a corpus luteum that secretes progesterone
- Uterus: Progesterone stimulates the endometrium to become even thicker and to develop more blood vessels and glands, ready to receive the embryo if an egg cell is fertilised
Day 23–28
Ovaries: If fertilisation does not take place:
• The corpus luteum shrinks and stops secreting progesterone
If fertilisation takes place:
- The corpus luteum remains active in the ovary and continues to secrete progesterone
- No more follicles develop in the ovaries
- No menstruation takes place
PDF Downloadable Notes on Menstrual cycle:
Question and Answers Activities:
Find short and long questions for Grade 12 Life Sciences, which will help you to prepare for the exams, tests, practical tasks, and assignments.
Questions

- Name the hormones A and B.
- Give reasons for your answers in question 1.
- What event occurs on day 14?
- Name the other two hormones involved in this cycle.
- Did fertilisation occur during the cycle shown in Figure 4.6?
- Explain your answer in question 5.
Answers
Answers to activity 3
- A – Oestrogen B – Progesterone
- A: The Graafian follicle secretes oestrogen /Oestrogen reaches
- its maximum level before ovulation.
- B: The corpus luteum produces progesterone /Progesterone reaches its maximum level after ovulation.
- Ovulation
- LH and FSH
- No
- Progesterone levels decrease, towards the end of the cycle.
More Resources
https://byjus.com/biology/menstrual-cycle/