Female Reproductive System Grade 12 Life Sciences Notes with Activities. A female’s internal reproductive organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The vagina is a muscular, hollow tube that extends from the vaginal opening to the uterus. Because it has muscular walls, the vagina can expand and contract
Female Reproductive System Grade 12 Life Sciences Topics
The Female Reproductive System is a key topic in the Grade 12 Life Sciences curriculum in South Africa. The focus is on the structure and function of the female reproductive system, as well as the hormonal control of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
The following are the key aspects of the Female Reproductive System covered in the Grade 12 Life Sciences curriculum:
- Structure and Function of the Female Reproductive System: The curriculum covers the anatomy and physiology of the female reproductive system, including the ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, and vagina. Students learn about the role of each organ in the female reproductive system, as well as the process of oogenesis and fertilization.
- Hormonal Control of the Menstrual Cycle: The curriculum covers the hormonal control of the menstrual cycle, including the role of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovaries. Students learn about the different phases of the menstrual cycle, including the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase.
- Pregnancy and Birth: The curriculum covers the process of fertilization, implantation, and embryonic development. Students learn about the hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy, as well as the stages of labor and delivery.
- Reproductive Health: The curriculum emphasizes the importance of reproductive health and the prevention of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Students learn about the different types of STIs, as well as the methods of prevention and treatment.
Video: Life Sciences: Female Reproductive System: Fallopian Tube and Uterus
The Grade 12 Life Sciences curriculum in South Africa covers the Female Reproductive System in detail, emphasizing the structure and function of the female reproductive system, the hormonal control of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy, and the importance of reproductive health. This topic is essential for understanding the human body and is critical for students pursuing careers in healthcare and medicine.
Female Reproductive system Grade 12 Life Sciences Notes
Female Reproductive system Grade 12 Life Sciences Notes (pdf downloadable):
- Gr-12-LS-Topic-4-Human-Reproduction_2021_Workbook_RL-1
- 1854_fdoc-1
- Human-Reproduction-1-Male-and-Female-Puberty-and-Gametogenesis
- 2021-Gr12-Life-Sciences-wkbk-1
- Life-Sciences-Reproduction-and-Endocrine-System-and-Homeostasis-
- Life-Sciences-FET
- Grade-12-Life-Science-Human-Reproduction-Notes
- 2021-Gr12-Life-Sciences-wkbk
- Human-Reproduction-1-Male-and-Female-Puberty-and-Gametogenesis
The different parts of the female reproductive system and their functions.
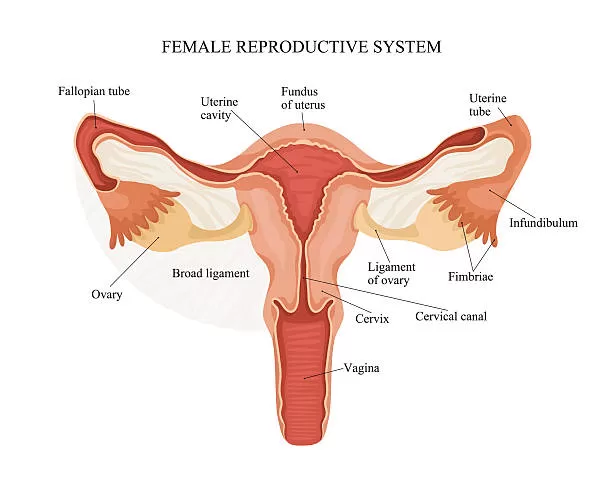
- Fallopian tube: Connects the ovaries to the uterus, transports egg cells from the ovary; it is the site of fertilisation
- Ovary: Produces egg cells, secretes progesterone and oestrogen
- Vagina: Receives the penis and semen during sexual intercourse; it is the passage through which the baby is born
- Uterus: Carries the embryo and foetus during pregnancy
- Endometrium: Inner lining of uterus; place where the embryo implants and the placenta forms
- Cervix: Lower, narrow part of uterus. It stretches to allow the baby through during childbirth
Female Reproductive System Grade 12: Question and Answers Activities:
Find short and long questions for Grade 12 Life Sciences, which will help you to prepare for the exams, tests, practical tasks, and assignments.
Questions & Answers
Here are five sample questions and answers related to the Female Reproductive System in the Grade 12 Life Sciences curriculum in South Africa:
1. What is the role of the corpus luteum in the menstrual cycle?
Answer: The corpus luteum is a temporary endocrine structure that forms in the ovary after ovulation. It secretes progesterone, which is important for maintaining the endometrium in preparation for implantation of a fertilized egg. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum breaks down, leading to a drop in progesterone levels, which triggers menstruation.
2. What is the difference between an ovum and an oocyte?
Answer: An oocyte is an immature egg cell, which develops in the ovary. It undergoes meiosis to become an ovum, which is a mature egg cell that can be fertilized by sperm.
3. What is the role of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in the menstrual cycle?
Answer: FSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates the growth and development of follicles in the ovary. It also stimulates the production of estrogen by the developing follicles, which is important for preparing the endometrium for implantation.
4. What are the three layers of the uterus?
Answer: The three layers of the uterus are the endometrium, the myometrium, and the perimetrium. The endometrium is the innermost layer, which thickens and sheds during the menstrual cycle. The myometrium is the middle layer, which consists of smooth muscle and is responsible for contracting during labor. The perimetrium is the outermost layer, which is a serous membrane that covers the uterus.
5. What are the benefits of breastfeeding for both the mother and the baby?
Answer: Breastfeeding provides a range of benefits for both the mother and the baby. For the baby, breastfeeding provides essential nutrients, antibodies, and hormones that support growth and development. It also reduces the risk of infections, allergies, and chronic diseases. For the mother, breastfeeding promotes bonding with the baby, reduces the risk of postpartum bleeding, and may reduce the risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
6. What is the role of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in pregnancy?
Answer: hCG is produced by the placenta during pregnancy and plays a critical role in maintaining the corpus luteum in the ovary. This is important because the corpus luteum secretes progesterone, which is necessary to maintain the endometrium and support the developing embryo. hCG also stimulates the production of estrogen, which is important for fetal development.
7. What is the function of the cervix?
Answer: The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that protrudes into the vagina. Its main function is to act as a barrier between the vagina and the uterus, protecting the uterus from infections. The cervix also produces mucus that changes in consistency during the menstrual cycle, which helps sperm travel through the cervix and into the uterus.
8. What is the difference between a zygote and a blastocyst?
Answer: A zygote is the single cell that forms when a sperm fertilizes an egg. It undergoes several cell divisions to form a blastocyst, which is a hollow ball of cells that implants in the uterine wall. The blastocyst consists of an outer layer of cells that form the placenta and an inner cell mass that forms the embryo.
9. What are the potential side effects of hormonal birth control?
Answer: The potential side effects of hormonal birth control include nausea, headaches, breast tenderness, mood changes, and changes in menstrual bleeding patterns. Some women may also experience more serious side effects, such as blood clots, which can be life-threatening.
10. How do sexually transmitted infections (STIs) affect the female reproductive system?
Answer: STIs can have a range of effects on the female reproductive system, depending on the type of infection. They can cause inflammation of the reproductive organs, leading to pain, discomfort, and scarring. STIs can also increase the risk of infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and other complications. Some STIs, such as human papillomavirus (HPV), can increase the risk of cervical cancer.
