Nucleic Acids Life Sciences Grade 12 Questions and Answers
NUCLEIC ACIDS – LIFE SCIENCES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Activity 1
- A DNA molecule contains 600 nitrogen bases. If 20% of this is adenine, determine the number of each nitrogen base in the DNA molecule. (3)
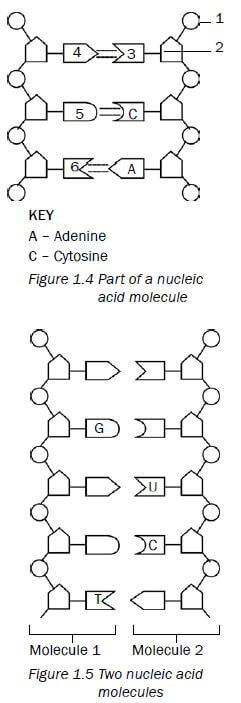
- Figure 1.4 (below) represents part of a nucleic acid molecule. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
2.1 Identify the nucleic acid shown in Figure 1.4. (1)
2.2 Label the following: (drawing below)- Part 1 (1)
- Part 2 (1)
- The nitrogenous bases 4, 5 and 6 (3)
2.3 What is the collective name for the parts numbered 1, 2 and 3?(1)
- Questions 3.1 and 3.2 are based on Figure 1.5 (below). This is a diagrammatic representation of a part of two different nucleic acid molecules found in the cells of organisms during a stage in the process of protein synthesis.
3.1 Name the molecules 1 and 2. (2)
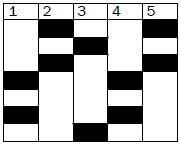
3.2 Give a reason for your answer in question 3.1. (2) - The result of profiling various DNA samples in a criminal investigation is shown below
 (Key below}
(Key below}
4.1 Was suspect X or suspect Y involved in the crime? (1)
4.2 Does the DNA of the suspect (from answer 4.1) match the first or second sample? (2) [17]
| Key for question 4: | Drawings for Q2 and Q3 above |
|  |
Answers to activity 1
- 20% adenine = 20% thymine✔ 30% cytosine✔= 30% guanine✔
20 × 600 = 120A = 120T 30 × 600 = 180C = 180G (3)
100 100 - 2.1 DNA✔
2.2- Phosphate✔ group (1)
- Deoxyribose✔sugar (1)
- 4 – adenine (A)✔
6 – thymine✔
5 – guanine (G)✔ (3)
2.3 Nucleotide✔ (1)
- 3.1 1 – DNA 2 – mRNA/RNA✔ (2)
3.2 DNA contains the nitrogenous base thymine (T).✔
RNA contains the nitrogenous base uracil (U).✔ (2) - 4.1 Suspect X was involved. ✔(1)
4.2 The DNA of suspect X matches with the second sample. ✔✔ (2) [17]
- cid.
Activity 2
Question 1
Study Figure 1.7 (below), which shows the process of protein synthesis, and answer the questions.
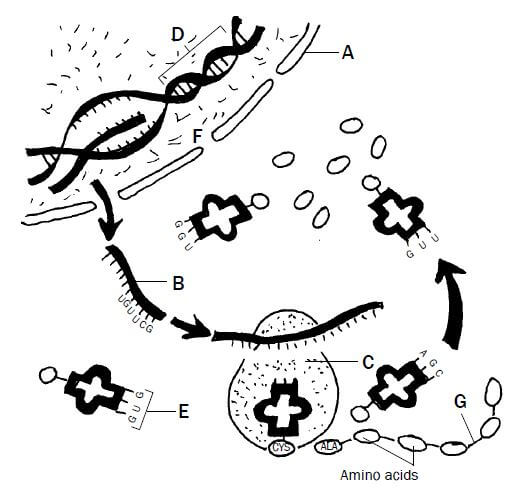
Figure 1.7 Protein synthesis
1.1 Label structures A, B and D. (3)
1.2 State ONE function of molecule D. (1)
1.3 Which stage of protein synthesis takes place at F? (1)
1.4 Identify organelle C. (1)
1.5 Name and describe the stage of protein synthesis that takes place at organelle C. (7)
1.6 Write down the codon of anticodon E from top to bottom. (1)
1.7 Name the type of bond (labelled G) between the amino acids. (1) [15]
Answers to question 1
1.1
A – Nuclear membrane✔
B – mRNA✔
D – DNA✔ (3)
1.2 Carrying hereditary characteristics from parents to their offspring✔ OR Controls the synthesis (manufacturing) of proteins✔ (1)
1.3 Transcription✔ (1)
1.4 Ribosome✔ (1)
1.5 Translation✔
- The mRNA strand from the nucleus becomes attached✔to a ribosome with its codons exposed
- each tRNA molecule carrying a specific amino acid✔
- according to its anticodon✔
- matches up with/complements the codon of the mRNA✔
- so that the amino acids are placed in the correct sequence✔
- adjacent amino acids are linked✔
- to form a protein✔ (7)
1.6 CAC✔ (the anticodon is GUG, so the complementary codon is CAC) (1)
1.7 Peptide Bond (1) [15]
Question 2
Table 1.3 below shows the DNA base triplets that code for different amino acids.
| Amino acid | Base triplet in DNA template |
| Leu (leucine) | GAA |
| His (histidine) | GTA |
| Lys (lysine) | TTT |
| Pro (proline) | GGG |
| Ala (alanine) | CGA |
| Trp (tryptophan) | ACC |
| Phe (phenylalanine) | AAA |
| Gly (glycine) | CCT |
Table 1.3 Different amino acids and their DNA base triplets
The following is a part of a sequence of amino acids that forms a particular protein molecule:
| Ala | His | Trp | Leu | Lys |
2.1 Name the process by which mRNA is formed from a DNA template. (1)
2.2 How many mRNA codons would be involved in forming the portion of protein shown above? (1)
2.3 Write down the sequence of the first three mRNA codons (from left to right) for this portion of the protein. (3) [5]
Answers to question 2
2.1 Transcription✔ (1)
2.2 5✔ (1)
2.3 GCU✔- CAU✔- UGG✔ (3) [5]

 (Key below}
(Key below}